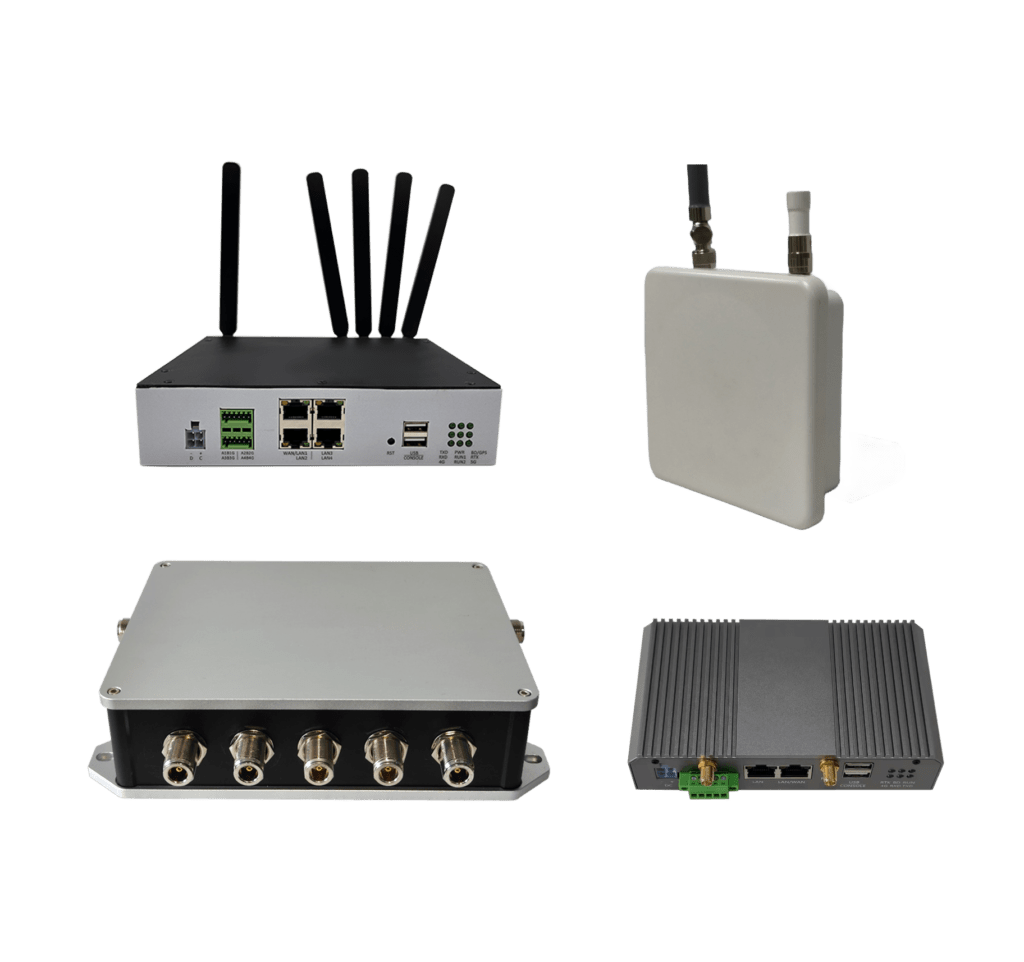
As industries embrace the full potential of 5G, new technologies like 5G LAN (Local Area Network) are redefining how devices connect, communicate, and collaborate. While 5G is commonly associated with fast internet on mobile phones, its real transformation lies in enterprise and industrial networks — particularly through the emergence of 5G LAN, a powerful alternative and enhancement to traditional wired or Wi-Fi-based LANs.
In this blog, we’ll explore what 5G LAN is, how it works, its key technical capabilities, and the practical use cases driving its adoption across sectors like smart manufacturing, logistics, ports, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) systems.
Оглавление
What Is 5G LAN?
5G LAN is a virtualized local area networking capability within a 5G network that allows multiple devices to be logically grouped and connected as if they were on the same Ethernet LAN — but without physical cabling.
Unlike traditional LANs that rely on Ethernet or Wi-Fi, 5G LAN uses 5G core network capabilities to create logical groups of devices. These devices can communicate directly with each other using low-latency, peer-to-peer (P2P) connections, even when located in different physical locations.
The concept is especially powerful in 5G private networks, where enterprises control their own 5G infrastructure. However, it can also be implemented over public 5G networks, depending on operator support.
Core Functions of 5G LAN
It provides many of the essential functions of a traditional LAN, enhanced by the flexibility and mobility of 5G:
1. Logical Grouping of Devices
Devices can be grouped into virtual LANs within the 5G network, enabling private and isolated communication among members of the same group — much like VLANs in Ethernet.
2. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Communication
With 5G LAN, devices can communicate directly and securely without routing through a central server or public internet, significantly reducing latency and traffic congestion.
3. Multicast and Broadcast Capabilities
5G LAN supports group communication, allowing one device to send data to multiple receivers simultaneously — ideal for synchronized operations or real-time alerts.
4. End-to-End Качество обслуживания (QoS)
QoS is managed across the network using 5G QoS identifiers (5QIs), ensuring high-priority traffic — such as control commands or video streams — is delivered reliably.
5. Isolation and Security
5G LAN enables network slicing and secure separation between groups or tenants, which is critical for enterprises with strict security or compliance requirements.
5G LAN vs. Traditional LAN
| Характеристика | Traditional LAN | 5G LAN |
| Deployment | Wired or Wi-Fi-based | Wireless over 5G |
| Mobility | Limited (fixed devices) | High (supports mobile devices and AGVs) |
| Латентность | Low, but limited by cabling and routing | Ultra-low with edge compute |
| Масштабируемость | Requires physical expansion | Logical and dynamic grouping |
| Безопасность | VLANs, firewalls | Native 5G isolation and slicing |
| Installation Time | Requires cabling and hardware | Wireless, faster to deploy |
While traditional LANs still have their place, especially in static environments, it provides an agile, scalable, and mobile alternative — especially suited for industrial and mission-critical applications.
Key Use Cases for 5G LAN in Industry
📦 1. Умное производство
Manufacturing plants are becoming increasingly automated and data-driven. It enables:
- В режиме реального времени coordination between robots and machines with low latency and reliable peer-to-peer communication.
- Предиктивное обслуживание, where sensors stream diagnostic data over a secure virtual LAN to edge processors.
- Mobile equipment networking, such as AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles), that require continuous connectivity while moving through a facility.
The wireless nature of 5G LAN reduces the need for physical cabling in dynamic factory environments, allowing faster reconfiguration of production lines.
🚗 2. V2X and Smart Transportation
In connected vehicle ecosystems, Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication is essential for safety and efficiency. It supports:
- Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) links, such as traffic signals or road-side units (RSUs), enabling intelligent traffic control.
- Low-latency communication for real-time decisions, which is not feasible with cloud-based routing.
Because it supports group communication and localized data processing, it is ideal for dense urban environments where vehicles, pedestrians, and infrastructure must collaborate in milliseconds.
⚙️ 3. Ports, Mining, and Logistics
Harsh industrial environments like ports, container yards, and mines require rugged, flexible networking solutions. 5G LAN enables:
- Coordination of heavy machinery (e.g., cranes, forklifts, autonomous haulers) in real-time.
- Wireless control of sensors and surveillance devices with fast deployment.
- Isolated virtual networks for third-party contractors or remote operations.
Replacing or supplementing fiber optics with it reduces installation costs and increases operational agility in vast or dynamic areas.
🏢 4. Smart Campuses and Enterprises
Large campuses can replace legacy Wi-Fi or Ethernet LANs with a private 5G LAN, providing:
- Secure and isolated staff networks, with BYOD (bring-your-own-device) support.
- Flexible deployment for temporary events, such as conferences or exhibitions.
- Visitor segmentation, where guests are assigned to separate logical networks.
Since it provides VLAN-like capabilities natively within the 5G network, it simplifies network management and improves segmentation security.
🛡️ 5. Emergency and Tactical Networks
In disaster response or military scenarios, rapid and reliable networking is critical. 5G LAN allows:
- Instant setup of ad-hoc communication networks, even in remote locations.
- Peer communication between field devices (e.g., drones, bodycams, sensors).
- High security and isolation, without relying on public infrastructure.
Deploying mobile 5G LAN systems with edge computing can transform command-and-control capabilities in field operations.
Benefits of TruGem 5G Gateways with 5G LAN
Let’s summarize the key benefits:
✅ High Flexibility
No physical cabling needed. Devices can be logically grouped and regrouped as needed, supporting agile operations.
✅ Сверхнизкая задержка
Peer-to-peer communication within the 5G network enables fast response times, critical for time-sensitive applications.
✅ Повышенная безопасность
With native slicing and user-level isolation, it provides enterprise-grade security for mission-critical environments.
✅ Seamless Mobility
Supports mobile assets (like AGVs, vehicles, or handhelds) while maintaining session continuity.
✅ Easy Integration
Supports existing network protocols and integrates with edge computing platforms and private 5G cores.
Considerations Before Deploying 5G LAN
- Infrastructure Readiness: it often requires a 5G Standalone (SA) core network and MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) support.
- Device Compatibility: Connected devices must support 5G and relevant security policies.
- Spectrum and Licensing: Private 5G deployments depend on regulatory environments and spectrum availability.
- Network Slicing Strategy: Logical isolation and QoS need to be planned in advance to support multiple tenants or services.
Заключение
5G LAN is a breakthrough networking model that extends the capabilities of traditional LANs with the power of 5G. By combining низкая задержка, mobility, scalability, and security, it empowers industries to modernize their connectivity infrastructure without the limitations of physical cabling.
Whether you’re running a smart factory, operating autonomous vehicles, or managing critical infrastructure in remote environments, it offers a future-proof, flexible solution that adapts to your needs.
As 5G Standalone networks and private 5G deployments continue to expand, It will play a central role in enabling next-generation industrial and enterprise connectivity.
Вопросы и ответы:
It is a virtual networking capability within 5G networks that allows devices to be grouped into isolated, low-latency, secure networks — similar to Ethernet LANs but without physical cabling. It supports mobility and wireless deployment, which traditional LANs do not.
It can be implemented in both public and private 5G networks. However, private networks typically offer more control, customization, and performance guarantees for enterprise applications.
Industries such as smart manufacturing, logistics, transportation (V2X), energy, mining, and smart cities benefit greatly due to their need for low-latency, mobile, and secure device communication.
Yes. Devices must support 5G connectivity and be compatible with the network’s slicing and security mechanisms. A 5G Standalone (SA) core and edge computing infrastructure are often required for full functionality.
Absolutely. 5G LAN offers strong security features, including traffic isolation, network slicing, and QoS controls, making it suitable for mission-critical and safety-sensitive operations.

