The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed industries by connecting devices to collect and exchange data. Building on IoT’s foundation, Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) integrates AI to bring intelligence and adaptability to these systems. As businesses embrace advanced technologies for efficiency, it’s crucial to understand the differences between IoT and AIoT and their implications for applications like IoT device management, industrial monitoring, and edge computing then.
Table of contents
What is IoT (Internet of Things)?
IoT refers to a network of connected devices equipped with sensors that gather and share data over the internet.
- Key Features: IoT devices enable real-time monitoring and automation of processes, relying on centralized platforms for data analysis.
- Applications: From smart homes and wearable devices to industrial IoT solutions, IoT has revolutionized industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. For example, IoT device monitoring and control allow for streamlined operations across connected ecosystems.
What is AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things)?
AIoT enhances IoT by embedding artificial intelligence into connected systems, allowing devices to analyze real-time data and make intelligent decisions autonomously.
- Key Features: AIoT leverages predictive analytics to provide insights beyond mere data collection, enabling smart and autonomous systems.
- Applications: Examples include AIoT solutions for autonomous vehicles, smart factories, and edge computing in industrial applications, where real-time decisions are made locally with data collection and analysis.
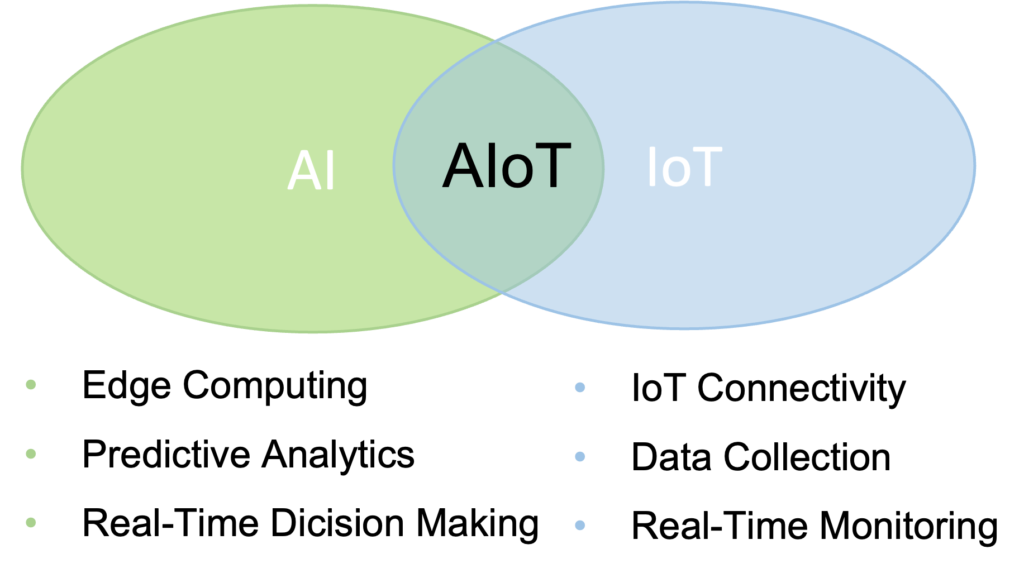
Key Differences Between IoT and AIoT
- Data Processing and Analysis
- IoT: Relies on centralized platforms like cloud-based IoT platforms to collect and process data. Data is sent to a remote server, leading to potential latency issues.
- AIoT: Incorporates edge computing, allowing devices to process data locally. This reduces latency and enables instant decision-making, critical for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles or industrial robotics.
- Automation and Intelligence
- IoT: Supports basic rule-based automation. For instance, it can trigger a notification when a specific threshold is crossed in an industrial setting.
- AIoT: Leverages AI to deliver intelligent automation. AIoT solutions can adapt dynamically to changing patterns, such as optimizing logistics routes or detecting anomalies in complex systems.
- Scalability and Efficiency
- IoT: Scaling IoT systems often introduces challenges like increased bandwidth consumption and reduced efficiency, especially when managing vast amounts of real-time data.
- AIoT: Scales effectively by processing data on the edge, minimizing bandwidth needs while maintaining efficiency. AIoT thrives in large-scale applications such as smart cities and industrial IoT device management.
- Applications and Use Cases
- IoT: Focused on monitoring and control applications, such as smart home devices and IoT device monitoring for equipment.
- AIoT: Designed for intelligent, predictive, and autonomous applications. Examples include predictive maintenance in manufacturing, geofencing for fleet management, and intelligent traffic control in urban areas.
IoT vs AIoT
Benefits of AIoT Over Traditional IoT
- Enhanced Efficiency and Automation AIoT eliminates inefficiencies by processing real-time data directly on devices, enabling instant and precise responses. This makes AIoT an ideal solution for complex scenarios like real-time traffic management or supply chain optimization consequently.
- Improved Decision-Making AIoT leverages machine learning and predictive analytics to transform raw data into actionable insights. For instance, in industrial applications of IoT, AIoT can predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Cost Savings and Scalability By reducing reliance on centralized cloud computing, AIoT lowers operational costs. Its scalability supports industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics, where large-scale operations require high efficiency.
- Advanced Security AIoT enhances security with intelligent algorithms capable of detecting and mitigating potential cybersecurity threats. IoT alone relies on basic security measures, which may not suffice in high-stakes environments like smart grids or financial IoT solutions though.
- Support for Cutting-Edge Technologies AIoT seamlessly integrates with technologies like 5G and edge computing, empowering next-generation applications. Examples include autonomous systems, AIoT-powered robotics, and remote industrial monitoring.
AIoT transcends IoT by bringing intelligence, real-time decision-making, and scalability to connected ecosystems. It’s the future of IoT technology, offering unmatched benefits for industries seeking innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About AIoT and IoT
IoT (Internet of Things)
Core Focus: The core of IoT is device connectivity and data collection, but it does not necessarily involve complex data processing or analysis.
Applications: IoT is widely used in smart homes, smart cities, health monitoring, and other fields.
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things)
Core Focus: IIoT systems often require higher reliability, security, and real-time performance because they are usually related to critical industrial operations.
Applications: IIoT is commonly using for improving production efficiency, equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, etc.
AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things)
Core Focus: AIoT not only includes device connectivity and data collection but also involves the use of machine learning, data analysis, and other AI technologies to analyze data, thereby achieving automated decision-making and optimization.
Applications: AIoT is applying to various fields such as intelligent transportation systems, automated manufacturing, smart healthcare, etc. It provides more advanced intelligent services and solutions.
AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) impacts IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) data privacy and security in several significant ways.
Integration and Interoperability:
AIoT systems often need to integrate with IIoT devices and systems to provide comprehensive solutions.
This integration requires seamless communication and data exchange, which can introduce new security and privacy challenges accordingly.
Data Sharing and Collaboration:
In IIoT environments, data sharing among different devices and systems is crucial for efficient operations.
AIoT systems can facilitate this data sharing but must ensure that it is done securely to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of data.
Regulatory Compliance:
IIoT systems often operate in highly regulated industries such as manufacturing and healthcare.
AIoT systems must comply with these regulations to ensure data privacy and security, which can be challenging due to the complexity and interconnected nature of these systems.
One specific example of an AIoT application in a smart city is a smart lighting system. IoT sensors can detect the presence of people and vehicles, and AI algorithms can adjust lighting levels accordingly. This not only saves energy but also improves safety and security by ensuring that areas are well-lit when needed.
In summary, a smart city is a classic example of an AIoT application, where AI and IoT technologies are seamlessly integrated to enhance urban living, improve public services, and optimize resource usage. Click AIoT Solution to learn more.
The future of AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) is bright and filled with potential for growth and innovation. It’s characterized by rapid growth, technological advancements, and emerging applications across various industries. While challenges such as data security and privacy remain, the opportunities for innovation and societal impact are immense. With continued investment and collaboration, AIoT has the potential to transform the way we live, work, and interact with the world.
