For decades, the manufacturing world has been driven by a binary mindset: either automate a process entirely or rely on human operators. But as industrial environments become more dynamic, global pressures intensify, and product lifecycles shorten, this binary view no longer works. Factories need agility as much as they need precision. They need intelligence as much as they need speed. This is where Hybrid Automation—the strategic integration of human judgment with artificial intelligence and autonomous systems—enters the spotlight.
Manufacturing leaders are no longer asking whether automation should replace workers. They are asking: How can people and machines co-evolve to create a smarter, safer, and more flexible industrial ecosystem? In this new paradigm, the human becomes the strategist, the AI becomes the analyst, and the robot becomes the executor. Together, they form a synchronized operational model that is far more capable than any single actor alone.
Table of contents
- Why the Age of Full Automation Fell Short
- Hybrid Automation: A Redefinition of Industrial Capability
- The Strategic Drivers Behind Hybrid Automation
- How Human-AI Collaboration Works on the Factory Floor
- Scenarios Where Hybrid Automation Outperforms Full Automation
- The Workforce of the Future: AI-Augmented Talent
- Technologies Powering Hybrid Automation
- Challenges and How Industry Leaders Overcome Them
- The Strategic Impact of Hybrid Automation
- Conclusion: The Hybrid Era Is Here
Why the Age of Full Automation Fell Short
Early visions of automation promised factories with minimal human presence. However, practical experience revealed fundamental limitations: automated systems struggle with non-structured scenarios, unusual materials, unexpected variability, and novel tasks. While robots excel at repetition, humans excel at intuition and adaptation. For this reason, many manufacturers discovered that full automation produced unexpected inefficiencies—rigid workflows, costly engineering updates, and slow response to real-world disruptions.
This realization has accelerated a transition from traditional automation to Hybrid Automation, where Human-AI Collaboration forms the core of operational strategy. Instead of eliminating human involvement, industry innovators now focus on amplifying human capability with intelligent machines.
Hybrid Automation: A Redefinition of Industrial Capability
At its essence, Hybrid Automation blends the cognitive strengths of humans with the computational precision of AI and the operational consistency of robotics. It marks a shift from deterministic workflows toward Intelligent Workflows—systems that evolve through real-time learning, continuous optimization, and data-driven reasoning.
In modern factories:
- Humans provide contextual intelligence, situational awareness, and ethical judgment.
- AI provides pattern recognition, anomaly detection, predictive insights, and decision support.
- Robots provide physical execution, endurance, and precision.
Together, they create a closed feedback loop that adapts to uncertainty, complexity, and real-world variability.
This hybrid model does not merely enhance efficiency—it transforms the factory floor into a living system capable of self-correcting, predicting failures, reallocating resources, and optimizing outcomes dynamically.
The Strategic Drivers Behind Hybrid Automation
- Complexity of Modern Production
Products are becoming more customized, multi-versioned, and rapidly iterated. Fully automated systems cannot easily adapt to these fluctuating requirements. Humans remain essential for high-mix, low-volume production environments.
- Workforce Gaps and Skills Shortages
By 2030, the global manufacturing sector is expected to face millions of unfilled technical jobs. Hybrid Automation does not eliminate people; it elevates them by redirecting human effort from repetitive tasks to higher-value cognitive work.
- The Rise of Industrial AI Systems
Computer vision, machine reasoning, large language models, and predictive analytics are reaching industrial-grade reliability. These technologies can now support real-time decision-making, enabling adaptive manufacturing at scale.
How Human-AI Collaboration Works on the Factory Floor
Human-AI Collaboration manifests across four operational layers:
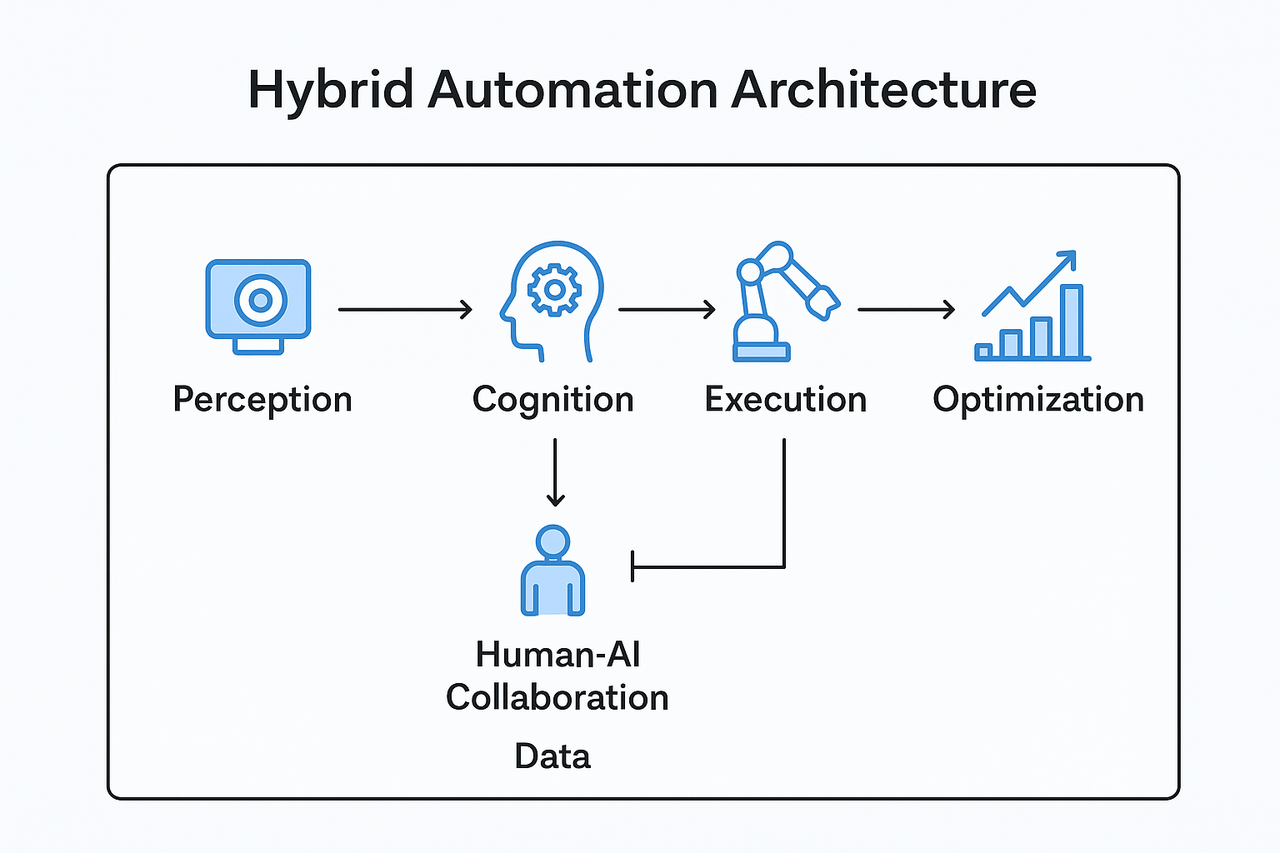
- Perception Layer – AI as the Eyes and Ears
AI-powered cameras, sensors, and edge computing nodes serve as the perceptual foundation. They generate:
- Object detection
- Defect classification
- Worker behavior recognition
- Equipment health metrics
- Environmental safety alerts
This sensing network continuously informs human operators and automated systems, enabling Intelligent Workflows that react to real-time conditions.
- Cognition Layer – Humans + AI Share Decision-Making
AI does not replace human decision-making; it augments it. Industrial AI Systems provide:
- Predictive maintenance alerts
- Root-cause analyses
- Process optimization suggestions
- Real-time quality scoring
- Risk forecasting
Humans interpret these insights, blend them with contextual understanding, and adjust production strategies accordingly.
This shared cognitive loop accelerates response times and reduces human error while preserving human judgment.
- Execution Layer – Robots Operate with Human Oversight
Collaborative robots (cobots), AGVs, autonomous forklifts, and robotic arms execute tasks such as:
- Precision assembly
- Repetitive movement
- Heavy lifting
- Palletizing
- Hazardous operations
Workers supervise, program, and guide these robots, ensuring safety and accuracy while robots handle labor-intensive work.
- Optimization Layer – Continuous Learning for Adaptive Manufacturing
AI continuously ingests data from equipment, workflows, and human input. Through machine learning models, the system:
- Learns from operator corrections
- Identifies inefficiencies
- Recommends workflow improvements
- Retrieves accumulated knowledge
- Aligns production plans with demand
This transforms factories into adaptive, evolving environments rather than static, rule-based systems.
Scenarios Where Hybrid Automation Outperforms Full Automation
- High-Variability Assembly
Electronics, automotive, and large equipment assembly rely heavily on human dexterity and decision-making. AI assists by guiding steps, verifying outcomes, and preventing errors.
- Quality Control Under Uncertain Conditions
Humans spot ambiguous defects; AI catches microscopic ones. Together, defect detection accuracy increases by over 40% in many industrial benchmarks.
- Safety-Critical Environments
AI monitors unsafe behavior, predicts equipment failures, and recognizes hazardous conditions. Humans evaluate risks and make final safety decisions.
- Changeovers and Rapid Reconfiguration
AI automates documentation, recommends parameter settings, and assists human technicians when switching from one product to another.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting
AI identifies anomalies; humans diagnose the mechanical or electrical root cause. This hybrid approach accelerates mean-time-to-repair (MTTR).
The Workforce of the Future: AI-Augmented Talent
Factories adopting Hybrid Automation report that employees become:
- More analytical
- More technology-savvy
- Less physically strained
- More focused on problem-solving
- More engaged in continuous improvement
New roles emerge:
- AI workflow technician
- Human-AI orchestration supervisor
- Data-enabled quality engineer
- Robot-human interaction specialist
- Industrial digital twin operator
These roles unlock human creativity while leveraging AI’s analytical power.
Technologies Powering Hybrid Automation
Provides low-latency processing for AI-driven tasks at the factory edge.
- Computer Vision Systems
Enable real-time detection of defects, safety risks, and workflow anomalies.
- Collaborative Robots
Designed for safe, close-proximity work with human operators.
- Digital Twins
Simulate workflows, optimize layouts, and predict operational risks.
- Industrial LLMs
Assist with troubleshooting, SOP generation, and task-level decision support.
Challenges and How Industry Leaders Overcome Them
Even though Hybrid Automation is powerful, manufacturers must address:
- Workflow Integration
Human-AI Collaboration requires careful orchestration, not simply adding robots or AI.
- Training and Culture
Workers must feel empowered—not threatened—by AI-enhanced tools.
- Data Quality
AI relies on accurate, clean, and timely data streams.
- Safety Governance
Hybrid environments require elevated safety standards for human-robot coexistence.
Industry pioneers overcome these hurdles by emphasizing transparency, investing in training, and adopting incremental deployment strategies.
The Strategic Impact of Hybrid Automation
Manufacturers embracing Hybrid Automation report measurable improvements:
- 30–50% faster defect detection
- 20–40% lower operational downtime
- 25–60% efficiency gains
- 40–70% reduction in safety incidents
- 30–55% more flexible changeovers
In global markets defined by volatility and customization, these advantages translate into lasting competitive differentiation.
Conclusion: The Hybrid Era Is Here
The future of manufacturing is not autonomous—and it is not manual. It is Hybrid Automation, where humans and machines operate in harmony, co-learning, co-adapting, and co-evolving. This model scales intelligence across the factory floor, strengthens resilience, accelerates productivity, and elevates the role of the human worker.
The factories that thrive will be those that acknowledge a simple truth: automation does not succeed by replacing people—it succeeds by empowering them.
